What Is Common Stock? Definition and How to Invest
When you buy stock in a company, you buy a percentage ownership of that business. How much of the business your one share buys depends on the total common stock outstanding, a figure you can easily determine using the company’s balance sheet. In general, common stock comes with the right to vote for corporate directors, as well as the right to vote on policy changes and stock splits. There are a few exceptions to this rule, however, such as companies that have two classes of common stock — one voting and one non-voting.
Common stocks: what they are and why you should care
A company’s share price is often considered to be a representation of a firm’s equity position. Looking at the same period one year earlier, we can see that the year-over-year (YOY) change in equity was an increase of $9.5 billion. The balance sheet shows this increase is due to a decrease in liabilities larger than the decrease in assets. If you’re very new to investing, you might still be getting familiar with what a stock is — and you might be distressed to find that there are, in fact, several different types of stocks.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
- Preferred stock may be less volatile but have a lower potential for returns.
- Stocks are also classified by market capitalization into large-, mid-, and small-cap categories.
- The fixed dividends also stabilize the company’s balance sheet, making it more attractive to additional investors.
- Common shareholders have the most potential for profit, but they are also last in line when things go bad.
Companies fund their capital purchases with equity and borrowed capital. The equity capital/stockholders’ equity can also be viewed as a company’s net assets. You can calculate this by subtracting the total assets from the total liabilities. For this reason, many investors view companies with negative shareholder equity as risky or unsafe investments. Shareholder equity alone is not a definitive indicator of a company’s financial health.
How To Calculate Stockholders’ Equity
It happens when a company buys shares of its own stock from other investors. Since repurchased shares can no longer trade in the markets, treasury stock must be deducted from shareholders’ equity. The fundamental accounting equation states that the total assets belonging to a company must always be equal to the sum of its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity. Personal finance advisors and financial advisors often guide their clients through the purchase or sale of a variety of company common stocks. Stockbrokers, too, facilitate the buying and selling of these common stocks.
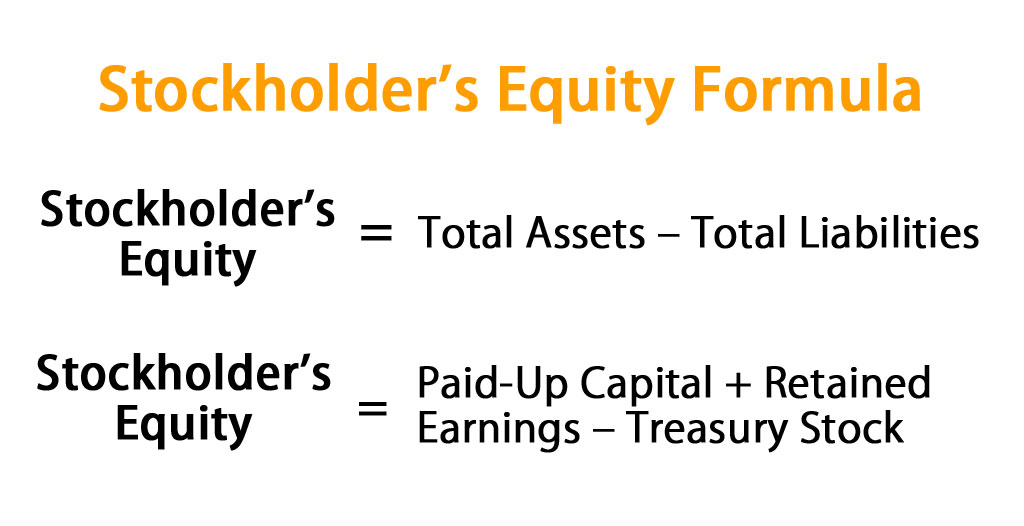
If it is positive, it means the business will survive for a long time. In contrast, if it is negative, it means the business has a short life span or cannot survive in the long term. For the survival of a business, assets should be more than liabilities.
How Do Stock Buybacks Impact Shareholders Equity?
However, they might still be less costly than the higher interest rates a company might have to pay to entice bond investors. Capital stock is an encompassing term referring to all types of shares, including both common and preferred stock, that a company can issue as stipulated by its corporate charter. It embodies the total ownership available for distribution among investors. Capital stock is listed on the balance sheet in the shareholder’s equity section and represents the company’s equity capital. Because common stocks are publicly traded, practically anyone can invest in them.
A good rule of thumb is to invest only what you can afford to lose, especially when you’re just starting. The stock market can be volatile, so it’s wise to keep a diversified portfolio and not put all your eggs in one basket. Risk premium is the additional return over the risk-free return which will compensate the investors for investing in a higher-risk asset. The capital asset pricing model is the relationship between the expected return and the risk attached. The expected return is equal to the return of risk-free assets plus the risk premium.
Preferred stocks are less dilutive of company ownership since they do not come with voting rights. They offer the issuing firm other benefits, not least because being less volatile makes them appeal to different investors. The fixed dividends also stabilize the company’s balance sheet, making it more attractive to additional investors. Another reason is that, for some companies, the cost of issuing preferred stock is lower than issuing bonds. Unlike interest payments on bonds, dividends on preferred stock are not mandatory and generally are not tax-deductible for the corporation.
Understanding a company’s financials is crucial to successful investing. From there, scroll down until you find the section in the 10-Q or 10-K called “Capital Stock.” All the details you need will be there. You’ll also see the various other stock categories, so don’t let that confuse you. One possible point of confusion we still need to mention is stock business performance report given to employees as compensation, typically in some combination of restricted stock, options, or equity grants. That stock should be included in the common stock outstanding figure. The life of common stock goes through a few phases, and understanding each step is important for putting the common-stock-outstanding number into proper perspective.
Once an IPO is complete, the common stock begins trading on the stock market. Like other securities, it is subject to market forces and price swings. Common stock is usually listed under “Stockholders’ Equity” on a balance sheet. The common stock account shows the value of all the common shares that have been given to shareholders.

